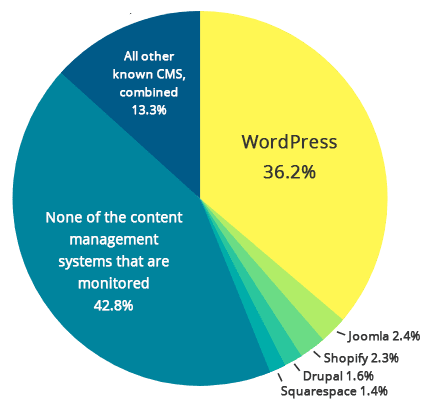
WordPress is a free and easy-to-learn website building platform that allows users to create web pages without any coding knowledge. It started as a blog hosting platform 18 years ago and has become the most popular content management system globally.
The latest version of WordPress has been downloaded more than 16 million times so far.
Google generates 1,360,000,000 results for the search, “What is WordPress?”
Today, it’s much more than just a platform to create your personal blog. Celebrities like Beyoncé and market giants like TED or Home Depot choose it to power their websites. We’ve prepared an extensive overview of the system, its benefits, and the reasons for its popularity.
WordPress Explained
WordPress (WP) is a free, open-source CMS (Content Management System). In other words, it’s a large PHP-based program that stores and displays your textual and visual data. This is why using WordPress is easy – you don’t have to worry about layouts, design, navigation, or SEO Services (Search Engine Optimization).
In simple words, the system architecture consists of three elements: core, theme, and plugin. WP’s most popular and attractive feature is its plugins. A plugin is an add-on for your WordPress site that improves and modifies the platform’s functionality. There are countless plugin options available on the Internet, either paid or free. If you know the exact functionality you need for your site, an add-on for it most likely already exists.
Themes change a WordPress website’s appearance – from simple color replacement on some elements to a complete redesign. If you take the same site and apply two different themes to it, only the content will remain the same, while the page will look completely different.
At the moment, the platform’s repository offers almost 59,000 official free plugins and almost 9,000 themes.
WP is equally popular among both beginners and experienced web developers. Due to its incredible popularity, it has a strong and massive global community. Whether it’s a “WordPress for dummies” walkthrough or a serious guide for advanced users – you can find support and solutions to almost any problem that might occur.
WordPress Today
Michel Valdrighi started WordPress as a platform for personal blogging and originally was called b2/cafelog. In 2003, the original platform hosted about 2,000 blogs. In 2003, Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little created WordPress as a fork to b2. By 2009, WP was recognized as the greatest brand strength of any open-source CMS.
Having gone through many changes, updates, and some security breach controversies, today, WP is the most successful content management platform; it powers 40% of all sites on the Internet and holds 65% of the global CMS market share. The Internet often compares Drupal vs. WordPress, but the platforms have rather different target audiences and objectives.
WP today is a fairly flexible system that is both beginner-friendly and can become a powerful instrument for those with knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. The platform still hosts millions of simple personal blogs. However, if you dig deeper, you’ll find out that huge corporations, world celebrities, Fortune 5000 companies, and the largest news outlets have their sites on WP. TechCrunch, NBC, USA Today, Disney, Spotify, Microsoft, and even the White House use it to power their pages.
Benefits of WordPress
WordPress describes its main advantages as four freedoms: to run the software for any purpose, to learn it and make changes, to redistribute, and to share your modified versions with the community. Let’s have a closer look at the system’s benefits.
WP Is Easy to Use
The first fact mentioned in any “WordPress for dummies” guide is its user-friendly interface. It refers to the simplified logic of user-platform interaction. It includes the navigation system and the way you add information to your WordPress site. It’s possible to learn how to find your way around the platform intuitively. WP started as a blog platform, and the creators retained the basic principles of easy content management.
The fifth version of WordPress introduced the Gutenberg visual editor that made the system even more user-friendly. As of now, Gutenberg is the primary tool for customizing and managing content. The editor suggests building pages out of functional blocks according to different tasks:
- Text content: headings, paragraphs, quotes, and lists
- Media files: separate pictures, galleries, audio recordings, and videos
- Integrating markup elements
- Hosting widgets and applications created by third-party developers
Each unit has its own settings, which users can change manually. For example, to share a social network post, you no longer need HTML code. Just select the corresponding block and specify the reference.
WordPress was one of the first actually newbie-friendly website-constructing tools. It means no coding knowledge is essential to create your first website.
WP Is Flexible
Whether you need a portfolio or an online shop – everything is possible on WP. As we mentioned before, there’s an incredible offer of plugins and themes to choose from. But it’s not the only way the system provides flexibility.
WordPress is fairly easy to expand and modify using features like custom post types and taxonomies. They allow creating an unlimited number of entity types (custom post types) and categorizing them by different criteria (taxonomies). It may be a bit more complex than the average “WordPress for dummies” guide, but it’s definitely possible to learn it.
For example:
- Employees (taxonomy: employees divided by departments within the company)
- Feedback (taxonomy: positive, negative)
- Items (taxonomy: categories of goods)
- Announcements (taxonomy: ad categories, etc.)
- Works or projects in a portfolio
Moreover, using the Meta Box framework, you can create custom fields to add extra information. For example, you can extend the Item description in your WP-powered online shop:
- Name of the item
- Brief description
- Main picture
- Full description
- Photo gallery
- Price
- Characteristics
- Terms of delivery
- In/out of stock, etc.
In general, you can find a plugin for any specific task – from SEO optimization to appointment bookings. And themes are often industry-specific. It means a medical service WordPress website will look very different from a food blog page.
WP Is Free and Open-Source
The project’s open-source nature created a massive community worldwide, which is considered one of the biggest benefits of WordPress. In reality, it means that if you face a problem using or customizing your WP page, there is someone out there who knows how to solve it. The WP community is famous for extensive documentation, educational materials, and great support.
Open-source also means that certain programming skills open up even more opportunities for customization and scalability. If you can’t find a plugin or a theme for your project’s specific needs, you may find that private developers or unofficial sources offer what you need.
In the case of getting any add-ons from unofficial sources, however, experts advise being very careful. Those extensions may contain malware, could lead to potential security vulnerabilities, or simply no longer support the next WP system update.
WP Is Optimized for Mobile Devices
Most WP themes have built-in, out-of-the-box mobile device optimization. There’s no need to go for special settings, acquire extra skills, or spend money on web development for your site’s optimization.
Using a flexible theme makes your website look great, regardless of the screen size that it appears on. This means that with the introduction of new screen sizes and the appearance of new formats, your website will be ready for processing without any additional work on your part.
WP Is Mature
WordPress has been around for 18 years. The advantage of using a more mature platform is that most bugs and vulnerabilities have already been fixed. Simply put, WP would not have survived to the present day if it had not been effective and useful. It’s an effective CMS with a long history of successful updates, and world-known brands use it to power their pages.
WordPress Site Types and Examples
WordPress today is no longer just a CMS for managing a simple blog. It’s evolved into a full, complex system with many features sufficient to create websites of any complexity. Let’s have a look at what pages you can build using the platform.
- Blog
You can create a WP blog using only basic functions without additional plugins. In this case, it’s recommended to use its main page to display the blog entries.
Famous examples: TechCrunch, Reuters Blog, PlayStation Blog, The Martha Blog
- Online Store
One of the most popular plugins for making an e-commerce site is WooCommerce. It doesn’t take long to set up the add-on, and you can find plenty of great tutorials to learn how to use it effectively.
Famous examples: Björk (official shop), House of Whisky Scotland, Bata, Marks & Spencer for Business
- Forum
bbPress is the official extension from WP developers that allows you to create and manage subscriptions, asynchronous discussions, and more.
Famous examples: CSS-Tricks Forums, Weddingbee, AngryBirdsNest
- Social Network
You can even create your own Facebook with your rules and regulations using WP. BuddyPress is your tool of choice to build online communities and create groups and teams.
- Web Portal
It’s an example of a more complex project combining several plugins. You can use bbPress to create forums and BuddyPress to implement social network activities and establish communication between users. And BuddyForms, for instance, will let your users post news entries. Incorporating Advanced Custom Fields will allow creating custom post and field types.
- Other Prominent examples
News and magazines: The New Yorker, Variety, The Sun, Vogue
Educational pages: University of Washington, Georgia State University, Lafayette College
Open-source and non-profit pages: Creative Commons, The Obama Foundation, Economic Policy Institute, Invisible children
Entertainment pages: AMC, Disney, MP3.com, BBC America, Pluto
How to Create a WordPress Site
The process of creating your first, simple website is fairly easy and doesn’t require too much time or advanced WordPress skills. Here’s our beginner guide on how to build your first WP page.
Step One: Choosing Hosting and Registering a Domain
If you are not planning to monetize your site immediately (which is a challenging task), you don’t have to pay for hosting. The free platform wordpress.com is sufficient for sharing cat pictures or starting your cookie-baking diary. More advanced users who are launching a commercial project, thematic blog, or a corporate site start with paid hosting.
First, you need to register a domain with a professional domain name. As a rule, the domain name should partially coincide with the site’s name, be short (so it’s not long and inconvenient for smartphone browsers), and have thematic meaning.
You can save time by choosing a hosting provider offering domain name registration and WP installation in one package. Otherwise, you need to go through a few extra steps manually:
- First, you need to download the WordPress package;
- Unpack the pre-downloaded WP archive and create a database on the server using your account on the hosting provider’s website;
- Enter login, password, and registration data, rename the file wp-config-sample.php to wp-config.php, and open it with a text editor, specifying the host and database with the password;
- Upload the files to the httpdocs folder and then unzip the distribution to the server;
- Next, you should directly install WordPress by filling in the required information fields and specifying search engine indexing requirements.
WordPress provides a detailed, beginner-friendly guide on the installation process.
Step Two: Choosing Themes
As we mentioned before, there are plenty of paid and free, official and unofficial options. Theme choice directly impacts the way your website looks and, possibly, how attractive it is for visitors.
Note the following:
- If you don’t need to develop a mobile version of the site, an adaptive layout template will be sufficient;
- Paid themes are less risky, regularly updated, and supported by the developers;
- Creating a WP site is easy and convenient, and it doesn’t take specific knowledge to manage or navigate the WP admin panel.
After installation, you can customize the theme: change the site’s name, add a menu panel, customize widgets, add and change pictures, etc.
Step Three: Choosing and Installing Plugins
Like with themes, there are thousands of options that address specific tasks. Less experienced users sometimes use too many unnecessary plugins, which slows down the site. However, the list of tasks that can be solved with basic WP functionality is very limited. And you will need some of the add-ons from the very beginning. For example, an SEO plugin to fill meta tags or the one that generates an XML site map. Only advice: don’t install the ones that are not necessary for your site’s functionality.
Some paid plugins are designed by companies that provide Custom Software Development Services. There are also options to order such services if your project has very specific objectives and you can’t find an existing suitable plugin.
Step Four: Creating Your First Post
The WordPress text editor has many tools for creating attractive posts – inserting images, lists, galleries, interactive elements. Content is divided into blocks, so it can conveniently handle different information types.
Step Five: What’s Next?
The previous four steps are merely the very basic introduction to creating the first WP site. Now it’s just new ideas and creativity. It includes changing the page’s looks, adding content, installing different plugins, and continuous experimenting.
Conclusion
People who have experience building a website on WordPress define it as beginner-friendly. However, the platform’s secret is that it’s a powerful instrument suitable for both newbies and experienced web developers. It provides an incredible number of ready-to-use templates and plugins for customization and solving particular tasks, which is great for beginners. At the same time, it offers a lot of freedom for creativity for those who know the code and create modified versions.