Cloud computing is slowly becoming the de facto business model for many companies. From startups to more established brands, everyone wants a piece of the Cloud. And it makes sense, too, since сloud computing affords a great deal of flexibility and advantages to clients worldwide.
But сloud computing, exemplified by the -as-a-Service (-aaS) suffix, is a complex and nuanced framework that has its advantages and drawbacks. As you begin to consider a сloud solution for your company, you should have a firm grasp of the differences and functionalities of the multiple cloud services available.
In this article, we will take a closer look at IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS, the three main categories of cloud computing. We will examine the characteristics of each model and how you can choose the right framework for your company.
Being armed with the right information, you will be able to make the right choice regarding which solution is best suited for your specific business requirements
IaaS vs. PaaS vs. Saas: What Are the Key Differences?
-as-a-Service, in itself, is pretty meaningless. It’s an appendix that needs and extra component to make it whole.
In today’s business world, particularly since cloud integration became a reality, you are likely to come across the terms IaaS PaaS SaaS. These are abbreviations for:
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
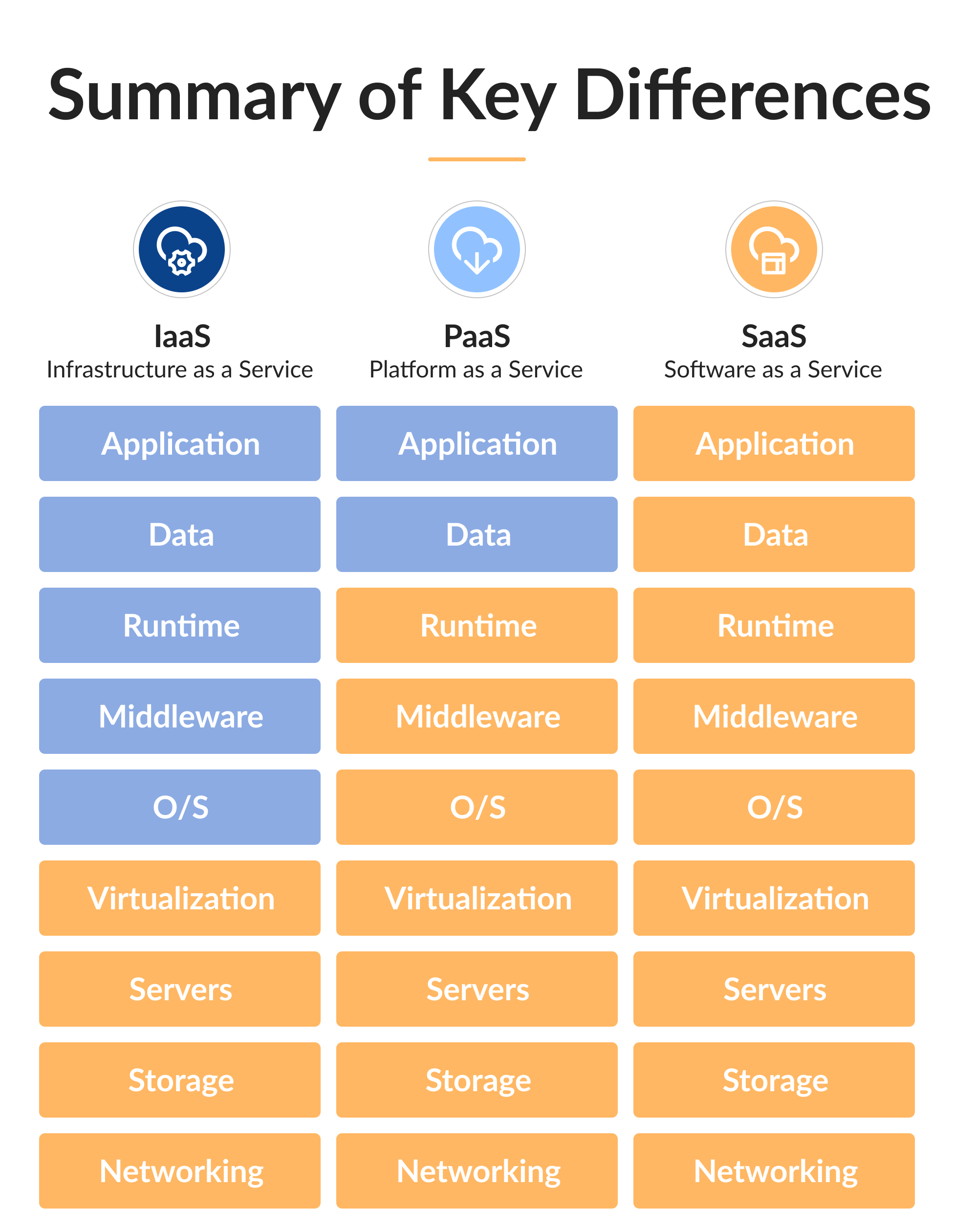
PaaS vs. Iaas vs. SaaS. These three acronyms form the backbone of Cloud-based computing today, each with its advantages and disadvantages over the rest, so it is up to the business owner to decide which cloud model is best suited to their business’ needs.
This schematic illustrates the subtle differences between these three concepts:
Each of these models can be easily accessed via any internet browser or applications. For instance, cloud computing makes it easier for your teams to collaborate using Google Sheets. This eliminates the need for you to upload and send a single file to different team members.
On the other hand, on-premises software requires to be installed on the computers within your workplace. This means the need for additional implementation, infrastructure, and work.
If you choose a cloud-computing service, all you have to do is to pay for your subscription and download the app if needed.
Now, that we have got the basics covered, let’s delve into this trio of acronyms a little deeper.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Definition: What Is SaaS?
What is SaaS meaning? A SaaS business model is a software delivery method that allows the distribution and access of data from any device with an internet connection.
Pros and Cons
What are the pros and cons of a SaaS business model?
Pros
Accessibility
One of the clearest advantages of SaaS is its accessibility. Users only need an internet connection and a web browser, or an app downloaded and installed on your device. This way, there is no need for a specialist to manually look for the installation of the product, which makes SaaS OS-agnostic and versatile.
Software updates
SaaS enables centralized software updates. That is, once the SaaS company deploys an update on the Cloud, every user can download it and update their software immediately. This facilitates a seamless business operation as there is no downtime or need for extensive security or compatibility testing, as would be the case with on-premises deployments.
No initial investment on hardware
Traditional deployments on-premise usually require a substantial financial outlay to acquire servers, network switches, and other expensive pieces of kit to create the necessary infrastructure to distribute software. Such setup usually leads to problems of compatibility between devices, software conflicts, etc.
A SaaS model does not require such infrastructure, as the software product can be deployed remotely and directly into the user’s device.
Reach
Global access to the internet means that SaaS deployments can potentially have a global reach. This greatly enhances a startup’s business opportunities while reducing costs and offering better expandability.
Better and more secure data handling
Traditional data storage solutions involve expensive hardware, plus maintenance & security & disaster recovery costs. Also, there’s always the possibility of hacking a central point of storage that might compromise a lot of data.
In a Cloud environment, data is continuously saved, providing a high degree of redundancy and integrity. An additional benefit is that a user’s data will be readily available even if they switch devices.
Cons
There are few drawbacks of SaaS applications.
Vendor-lock in
Some SaaS vendors are easy to sign up to, but difficult to end the contract with, which might lead to situations where porting to a different vendor might entail substantial charges and fees. Besides, not all vendors use a standard set of APIs and other tools, which might create conflicts and difficulties.
Limited Control
Your options for design and development will be entirely dependent on the boundaries of the PaaS solution. You will only be able to control the code of the app you create and not the framework behind it.
Limited choice of features
SaaS applications are usually provided ‘as is’; in other words, users do not have the opportunity to choose any features that they might want or need for their business.
When looking at IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS, you might notice that customization is relatively limited for SaaS models. Although some companies give you such options, you will still have to pick from what they offer – as opposed to tailoring a solution to your needs.
Over-reliance on the vendor for performance
SaaS users rely on the vendor for the system’s uptime and performance. Cyber attacks, downtime for maintenance, and other factors completely out of the users’ hands will affect the application’s reliance and performance.
SaaS Examples
We are already heavily relying on SaaS working models in our daily lives. Wondering which of the following is an example of SaaS you have at least once used? All of them are examples of SaaS.
- Google Apps
- Salesforce
- Dropbox
- MailChimp
- ZenDesk
- DocuSign
- Slack
- Hubspot
, and many more.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
Definition: What Is IaaS?
In cloud computing, IaaS delivers on-demand computing, networking, and storage resources over the internet, usually with a pay-as-you-go financial model. When considering IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS, many start-ups favor an IaaS due to its flexibility and convenience it offers. In simpler terms, it eliminates large monetary outlays to purchase expensive hardware outright.
Pros and Cons
What are the pros and cons of IaaS delivery?
Pros
Flexibility
This business model affords flexibility when a business needs it the most, as it enables start-ups, for example, to access a full hardware infrastructure at a fraction of the cost. You only need to purchase what you want at the moment – but you always have the option to expand based on your needs.
On-demand hardware purchases
Traditional deployments often involve the purchase of hardware components, which poses an inherent risk. What if these components turn out to be unsuitable for your needs? Maybe it’s too much hardware, or too powerful (and therefore, more expensive?)
Hardware acquisition in an IaaS business model is on-demand, in other words, what you need, when you need it.
Easy scalability
This relates to this business model’s flexibility. Startups usually begin small and grow exponentially, so it makes sense to use IaaS and focus on business growth during the company’s first few months of existence. Then, as the business expands, it’s easy to scale up due to IaaS as-you-need payment model.
System resilience
A ‘traditional’ organization must have robust and secure systems to ensure the continuous availability of its infrastructure. In other words, the business must be able to continue to operate. This puts pressure on IT departments.
IaaS provides resilience against outages that would hinder a business’s progress, as it is the system provider’s responsibility to maintain the network and guarantee uptime.
Cons
Security
Companies relying on the IaaS business model might face a dilemma over security, as they will have to trust the service provider with data handling. This might pose a security risk from a data privacy point of view, for example. Moreover, you will be in charge of any data stored. In case, there is a security threat and you lose valuable data, it will be your responsibility to recover it.
Over-reliance on the service provider
The relatively low cost and on-demand flexibility do have drawbacks. The startup has to completely rely on the service provider, security updates, and data management. Again, the question of customization is relevant here, as the latter is restrained depending on the specific IaaS provider you choose.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) IaaS
AWS EC2 is a prominent example of the IaaS business model, as it provides a scalable infrastructure solution for startups (or any other companies) that want to migrate their business to a cloud-based environment.
Develux features in-house AWS expertise and is able to offer practical advice and solutions for clients looking to evolve into the Cloud.
IaaS Examples
Some companies using an IaaS business model include:
- AWS EC2
- Rackspace
- Google Compute Engine (GCE)
- Digital Ocean
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Definition: What Is PaaS?
This type of cloud computing offering allows customers to develop, run, and manage applications on the Cloud, thus removing the inherent complexity of creating a computing infrastructure of their own.
If you compare IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS, you will probably consider PaaS a simpler version of IaaS. It can still serve its consumers with services such as storage solutions and servers. However, you will be using the infrastructure to develop a single application that you can deliver to your clients over the internet.
Similar to the other IaaS PaaS SaaS cloud categories, PaaS provides a secure platform for you to develop your solution on the internet.
Pros and Cons
What are the pros and cons of PaaS?
Pros
Minimal development
Because PaaS offers existing infrastructure, startups are faced with minimal requirements in terms of deployment, which leads to a rapid entrance to the market and a more substantial presence.
Scalability
The on-demand nature of PaaS enables careful planning and scalability of the solution. As more components are needed to address business growth, PaaS examples provide you with opportunities to leverage existing resources and expand them.
Cost-effective
PaaS offers a ‘ready-made’ solution, which significantly reduces operational costs. Such PaaS examples showcase that the business model is an excellent and viable choice for startups whose resources might be limited.
Quick deployment to market
Leveraging an existing infrastructure enables startups to ‘pick and choose’ existing components, help the company achieve market presence quicker, and save time and costs.
Cons
Vendor-lock in
As SaaS’s case, some vendors might be easy to sign up to, but difficult to end the contract with, which might lead to situations where porting to a different vendor might entail substantial charges and fees. Besides, not all vendors use a standard set of APIs and other tools, which might create conflicts and difficulties.
Data security and privacy
Companies relying on the IaaS business model might face data security and privacy issues, as in some cases, the PaaS vendor might host its databases with third-party companies. This might result in startups or other companies having their data compromised.
PaaS Examples
- WS Elastic Beanstalk
- Heroku
- Windows Azure (mostly used as PaaS)
- Force.com
- OpenShift
- Apache Stratos
- Magento Commerce Cloud
So Which -aas Model Is Best Suited to Your Business?
Being well informed of each of these business models’ advantages and drawbacks is only half the battle. Now you need to decide which of these three Cloud computing models (SaaS, IaaS, or PaaS) is best suited to what your business needs to do to thrive.
So it is time to take stock of your business, see where you are in your roadmap, and have a chat with your Chief Financial Officer to make a sound decision.
Limited resources (Small to large enterprises) – Definitely SaaS
SaaS is the safest choice for small and large enterprises that can call on limited resources, particularly at the start of their business journey. The reason for this is that SaaS enables clients to avoid significant financial expenditures at a crucial time. With SaaS, clients can access high-value hardware and software at a very affordable price.
Average resources (Medium to large enterprises) – Consider PaaS
Why? Minimal development, but high yield. Faster innovation. Scalability. If your business has average resources, PaaS offers a cost-effective and high degree of customization, while enabling a quick deployment to your target market.
Considerable resources (Medium to large enterprises) – IaaS is probably best for you
As resource availability grows, so do the opportunities. IaaS offers almost total control of the technology, plus great flexibility and cost-effective on-demand solutions, coupled with outstanding resilience.
When comparing IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS, it is evident that each model comes with its own specific features and advantages. Whether you are looking for storage solutions or a framework to develop customized applications, today, you can easily find a cloud platform that fits your bill.
It is best to be able to compare yourself SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS and choose an option because the future of business lies in the webs weaved by cloud solutions.
Summary: SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS
If you have read our guide, you now have an idea of the differences between IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS. There’s a risk of external management data issues conciliating the functionality you’re using with any service. But knowing the structure of each one will help you determine the right approach for your industry.
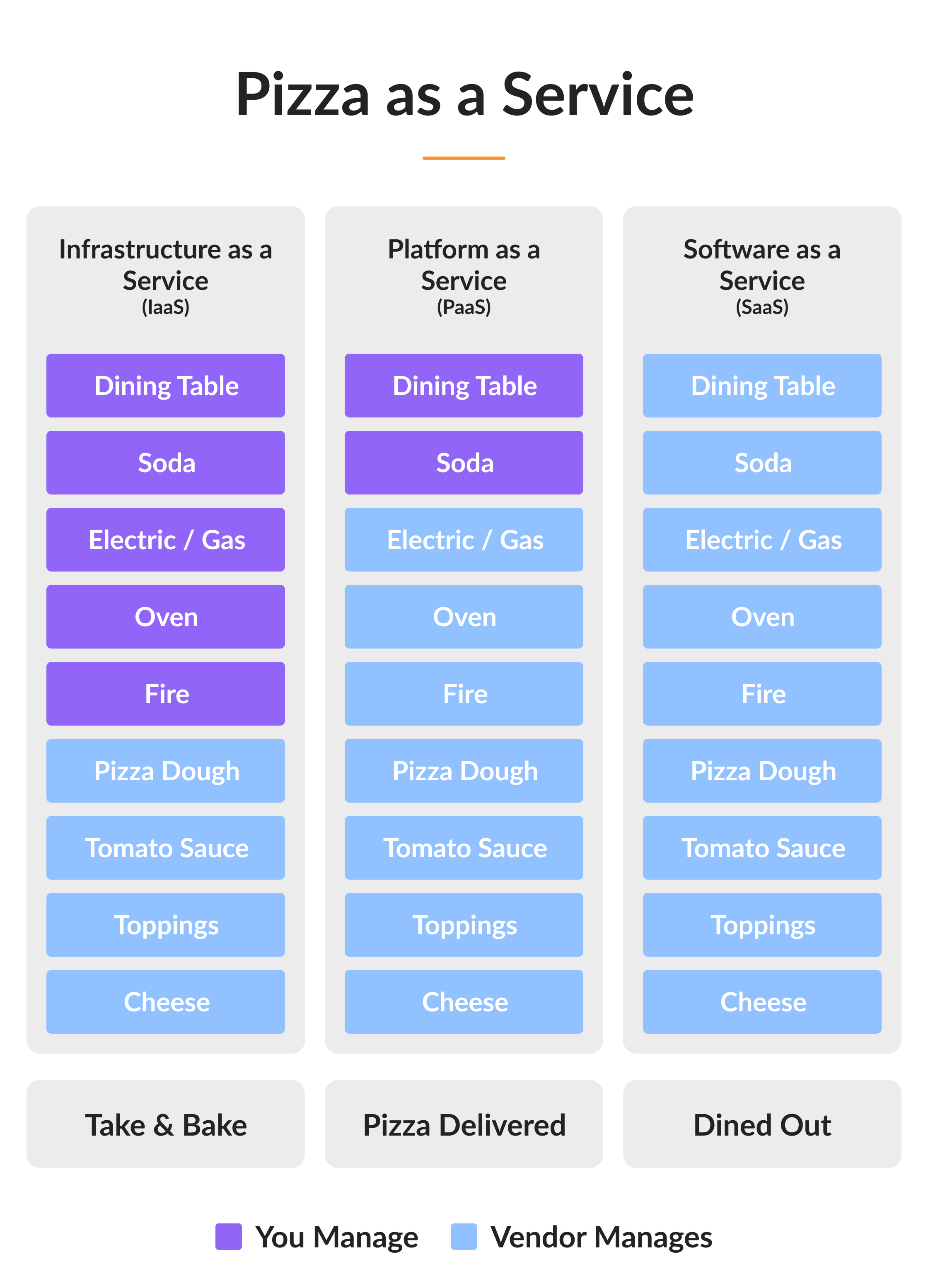
Now, let’s compare SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS like a Pizza Service.